If you have ever wondered what questions people are asking about your niche, what topics are trending or how interest shifts over time, Google Trends is a must‑use tool. It gives you a peek behind the curtain of search behaviour, what people search, when and where.
In this guide, you will learn to:
- Set up and navigate Google Trends
- Compare terms and visualise interest
- Spot seasonal trends and unexpected spikes
- Explore related queries and topics
- Use geographic data to localise your content
- Leverage Trends insights to inform campaigns
- Understand limitations and avoid common mistakes
- Know when to bring in a marketing strategist
By the end, you will not just be browsing trends. You will be using them to inform your content, digital adverts, product launches and overall marketing strategy.
What Is Google Trends?
Google Trends is a free tool from Google that displays how interest in search terms changes over time and across regions. It helps you spot emerging topics, seasonal patterns and audience preferences.
When you enter a search term, Google Trends returns a timeline of search interest, maps showing regional popularity, and lists of related queries and topics.
This insight helps you create content that resonates and reach people when they are most likely to search for your product or service.
Step 1: Access and Explore the Interface
Head to the Google Trends website to get started. You will see a search box and sections like Trending Searches, Year in Search, and programmer picks.
Begin by typing your keyword into the search bar. Google Trends will default to worldwide data over the past 12 months. You can then adjust:
- Region (Country or Global)
- Time range (Hour, Day, Year, Custom range)
- Category (Business, Health, etc)
- Search type (Web, Image, News, YouTube, or Shopping)
This flexibility is helpful for refining insights to your audience or marketing channel.
Step 2: Interpret the Interest Over Time Graph
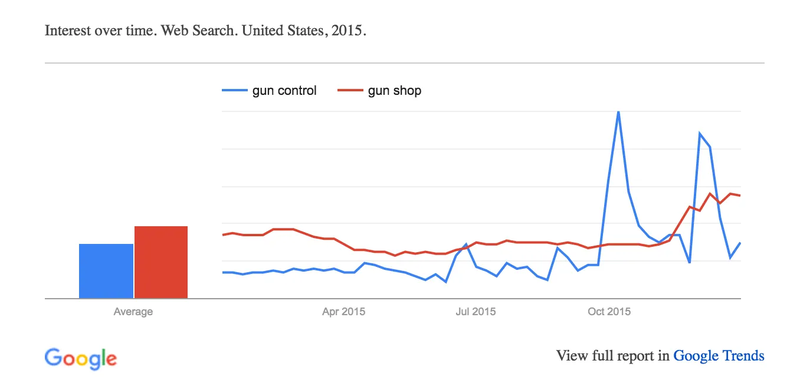
After entering a term like coffee or yoga, you will see a line graph labeled “Interest over time”. It shows relative search volume indexed from 0 to 100.
Higher peaks indicate higher interest compared to the highest point in that timeframe. Slight dips or flat sections do not mean zero interest, they simply reflect lower relative volume.
Look for patterns: recurring peaks (such as holiday shopping terms), steady upward trends (new industry interest) or sudden spikes (cultural moments or viral events).
Step 3: Compare Multiple Terms
Click Compare to add up to five search terms. For example, compare yoga mats versus pilates mats. Differences in peaks, consistency and seasonality provide clues about audience preference.
Make sure to keep comparisons relevant and easy to understand using clear search terms.
Step 4: Explore Regional Interest
Scroll down to see interest by region on a coloured map and in a list of top subregions.
This data helps you localise campaigns. For example, if interest in vegan recipes is stronger in Victoria than in New South Wales, you can tailor ads, content or offers for that region accordingly. If you’re scaling your team to handle regional campaigns, our marketing recruitment service can connect you with local talent across Australia.
Step 5: Discover Related Queries and Topics
At the bottom you will find related queries and topics.
Queries show other search terms that people searched at the same time. Topics are broader concepts people are linking to your search term.
Highly rising related queries often represent emerging opportunities. Top queries are established trends worth exploring regularly.
Step 6: Spot Seasonal Trends
Adjust the time range to several years to spot seasonality.
Common seasonal searches include tax, sunscreen, Halloween costumes or Christmas ideas. Recognising these patterns helps you publish content when people are searching, not after.
It is ready‑to‑go content that can drive traffic and engagement.
Step 7: Use Google Trends for Content and SEO
Google Trends can influence marketing strategy:
- Identify questions people ask and create targeted FAQs or blog pages
- Use rising topics as inspiration for new product or campaign ideas
- Plan seasonal content calendars in advance
- Validate your keywords and phrases for SEO
- Repurpose successful content across formats
For example, if “plant based recipes” is rising in summer, schedule summer recipe guides accordingly.
Step 8: Monitor Trends in Multiple Search Types
Beyond web searches, you can track trends in images, news, videos, shopping patterns and YouTube.
Use the drop down to refine results for each audience and format.
Step 9: Export and Share Data
Google Trends allows you to export data as CSV. This helps you analyse trends in more detail.
Export the interest over time, interest by region or related query data. You can merge this with Google Analytics or other tools to measure impact.
Share insights visually by embedding charts in reports, presentations or blog posts.
What Google Trends Cannot Show
It is important to be aware of limitations:
- Data is indexed, not absolute search volume
- Terms become compared relatively, not independently
- Only popular or trending searches are displayed, niche queries may not appear
- Rapid changes may not show immediately due to data refresh rates
- Data is aggregated, personal or user‑level analysis is not possible
Use Trends as a directional tool, not the only data source.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid these pitfalls when using Google Trends:
- Tracking the wrong seasonal timeframe
- Comparing broad and narrow terms unfairly
- Ignoring regional variance in search behaviour
- Overreacting to a short term spike as a long term trend
- Forgetting to adjust categories and search types
Know what the data means before acting on it.
Why You Might Hire a Marketing Strategist
Google Trends gives direction. A marketing strategist brings strategy.
A strategist will help you interpret the data in your business context. They can:
- Build seasonal campaigns based on search patterns
- Use related queries to form targeted content or landing pages
- Tailor messaging by region and audience interest
- Combine Trends insights with ads, SEO and analytics
- Confirm ideas before launching paid or organic campaigns
They turn data into action that drives leads, sales and engagement. If you’re not ready for a full-time hire, consider bringing on an SEO specialist or fractional CMO to apply these insights flexibly across your content or ad strategy.
Ready to start seeing results?
We connect businesses with marketing strategists who know how to use tools like Google Trends as part of a broader growth strategy.
Your strategist will not just show you graphs. They will build a plan, set priorities, refine content calendars and optimise campaigns. From content ideation to execution, they will apply data intelligently and drive results. Hire a marketing strategist through Cemoh today and let search insight shape your success.
